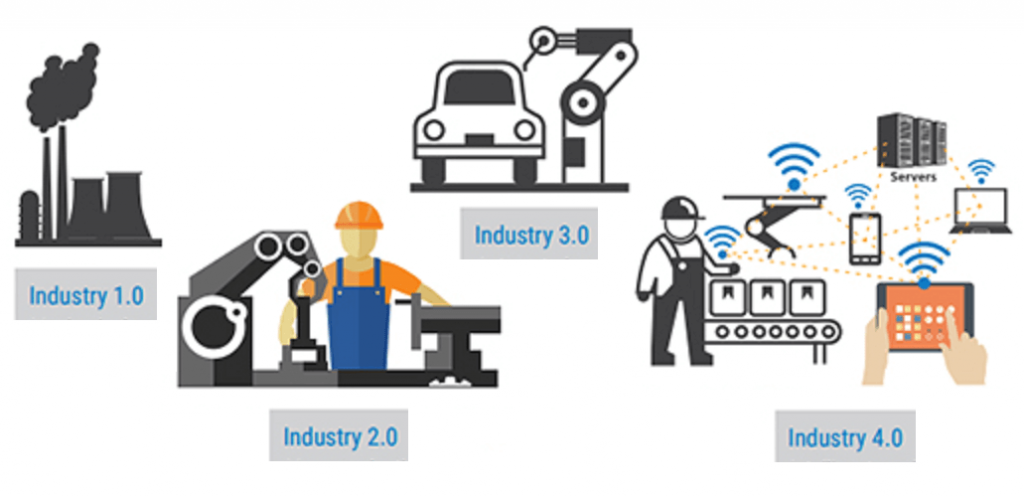
Industry 4.0 refers to adoption of cyber physical system like Internet of Things and Internet of system.
- 1st I.R- Used water and steam to mechanise production.
- 2nd I.R.- Used Electric Power to create mass production
- 3rd I.R- Used Electronics and I.T to automate.
- 4th I.R- Application of Information and Communication Technology ( Cyber Revolution, 4 IR)
This is the era of A.I, Biometrix, Renewable Energy, 3D printing, and one is witnessing merging capabilities of Humans and Machines.
Key Drivers
- High Speed Mobile Internet
- AI and Automation- Max impact on Human Race
- Data Analytics
- Cloud Technology
Implications of Industry 4.0
- Remote working
- Independent business decision
- Untapped potential
- Searching for mindset over skill
- Gig economy
- Recruitment industr
Challenges of Industry 4.0
- Loss Of Jobs And Inequality In Society
- Climate Concern
- Reduced Human Interaction
- Impacts Govt Policies
Work from Home
Any work done away from a physical work location. The Term has moved away from being an Option as Incentive to the New Norm.
Work from Home is known by various other terms such as Work from anywhere, Mobile work, Online, Telecommuting, Fexible Workplace, Virtual workplace, Working outside Office, Quarantine Workplace, Distributed Workplace.
Some of the benefits of work from home include:
- Increased Employee productivity
- Reduced turnover
- Lower Overhead Costs
- Reduntant jobs done away with
- Wider Talent Pool
Future of Remote Work – An Analytical Perspective
- Hybrid Model – (Incorporates mix of WFH and WFO).
- Ability of Employees to work away from Office.
- Work from Home
- Work from another location same city
- Work from another location in different geographies.
A Hybrid model is one in which an employee has to work two to three days from office and rest of the days from home. One can work from Co-Working spaces, Public Spaces. This model requires the presence of only Core Groups providing flexibility for rest. Most Organisations are still experimenting with this model.
Sectors with High Potential for Remote Work:
- Finance and Insurance.
- Management Consulting
- I.T.
- Communication such as PR, Branding.
- Teaching, Counseling
Sectors with High Potential for Remote Work: Entertainment, Recreation. Healthcare. Retail Trade. Mining. Manufacturing. Transportation and Warehousing. Food Sector, Agriculture.
Work from Home has ‘High Potential’ in developed Economies and requires ‘High Preparation’ in Emerging Economies.
References
Talwar R, Wells, S., Koury, A. and Rizzoli, A. (Eds) (2015) The Future of Business. UK: Fast Future Publishing ISBN 978-0-9932958-0-5
Rymarczyk, J., 2020. Technologies, opportunities and challenges of the industrial revolution 4.0: theoretical considerations. Entrepreneurial business and economics review, 8(1), pp.185-198.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.