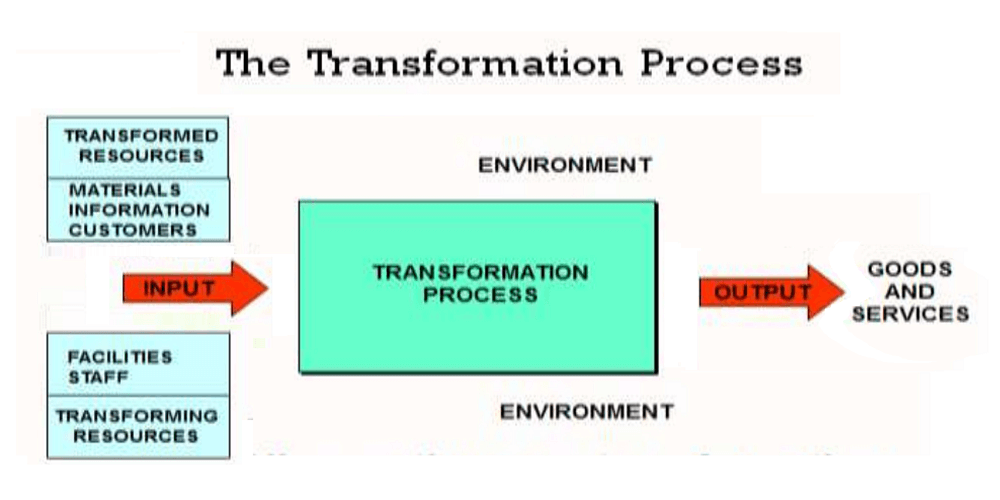
The transformation process refers to the series of activities that transform inputs into outputs and is a core concept in the study of operations management. This framework is commonly used in operations management to optimize the various processes and to streamline operations.
Introduction
The transformation process refers to the various activities that businesses undertake to transform inputs into outputs that are of greater value to customers.
The transformation process involves a variety of inputs, such as raw materials, information, customers, or services, and can produce a range of outputs, from finished products to improved customer experiences.
Understanding the transformation process is essential for businesses that are trying to optimize its operations.
Elements of the Transformation Process
The transformation process typically involves three key stages: inputs, transformation processes, and outputs.
Inputs are the resources that a business uses to create its products or services. These can include raw materials, labor, equipment, and technology. In a manufactuting firm, inputs might include raw materials such as wood, steel, or plastic, as well as labor and equipment.
Transformation processes are the activities that a business undertakes to convert inputs into outputs. These can include manufacturing, service provision, or information processing.
In the manufacturing industry, the transformation process might involve using raw materials to create a finished product. These processes might include cutting, shaping, and assembling these raw materials into finished products such as furniture, automobiles, or consumer electronics.
Outputs are the final products or services that a business produces, which are intended to meet the needs of customers, and are sold to them.
In the service industry, the transformation process might involve providing services to customers.
- Inputs might include customer needs and preferences, as well as the resources needed to provide the service, such as labor, equipment, and technology.
- Transformation processes might include activities such as consulting, design, or customer service.
- Outputs might include the service provided to the customer, such as financial planning, legal advice, or healthcare services.
Other Key Elements of the Transformation Process
In addition to inputs, transformation processes, outputs, other key elements of the transformation process includes feedback and control.
Control: Control is the process of monitoring and adjusting the transformation process to ensure it is running smoothly and that the resulting outputs meet customer needs and expectations.
Feedback: Feedback is the information that a business receives about its inputs, transformation processes, and outputs. It is essential to collect and analyze feedback effectively to identify areas for improvement and to ensure the process is meeting customer needs and expectations.
Types of Transformation Processes
The transformation process can be of four types: materials, information, customers, and services. Each type involves different inputs, transformation processes, and outputs.
Materials Transformation Process: Involves converting raw materials into finished products. Examples include manufacturing processes in industries such as automotive, construction, and consumer goods.
Information Transformation Process: Involves converting raw information into usable data. Examples include data entry, data processing, data analysis, data modeling, data visualization, and more, in industries such as finance, healthcare, and technology.
Customers Transformation Process: Involves changing the state of a customer, such as their appearance or mood. Examples include haircutting, spa services, and counseling in industries such as beauty, wellness, and mental health.
Services Transformation Process: Involves transforming the delivery of services to customers. Examples include transportation, hospitality, and education services.
Mapping the Transformation Process
Mapping the transformation process involves visualizing and analyzing the steps involved in converting inputs into outputs.
This can be done using a process map, which provides a visual representation of the transformation process. The process map should include the sequence of activities, the resources used, the information flow, and the feedback loops.
The process map can help identify inefficiencies in the transformation process, bottlenecks, and areas for improvement. It can also help businesses to understand the flow of activities, resources, and information, and to identify areas where communication and coordination can be improved.
To sum it up, the transformation process is a critical component of operations management, as it enables businesses to convert inputs into outputs that meet the needs of customers, while improving efficiency, enhancing quality, facilitating innovation, meeting customer needs, and supporting growth. By effectively managing the transformation process, businesses can optimize their operations, improve their overall performance, and gain a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website AcademicsHQ.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.