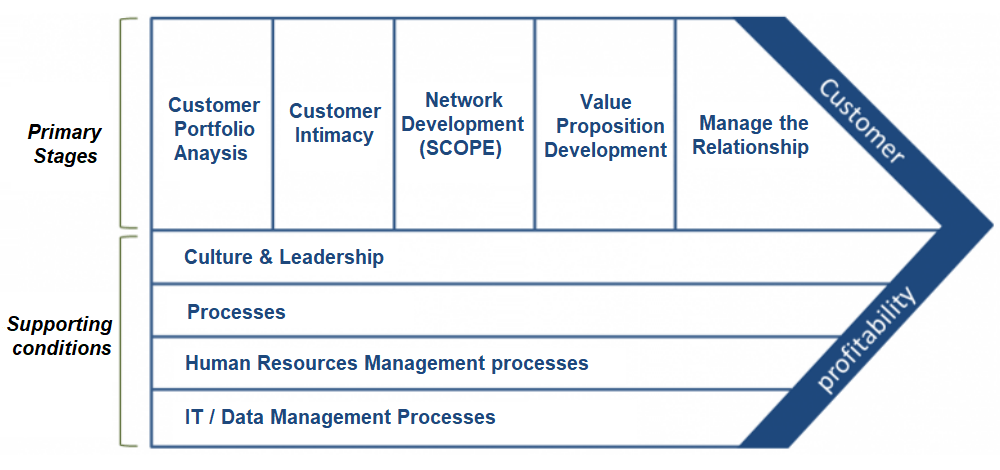
Francis Buttle’s Customer Value Chain outlines the stages involved in creating customer value and building profitable customer relationships within the context of customer relationship management (CRM).
Customer Value Chain provides a systematic means of displaying and categorizing value activities and margin.
At each stage in the value chain, there is an opportunity to contribute positively to the firm’s competitive strategy by performing an activity or process in a way that is better and or different than the competitors’ offer (Hollensen, 2011).
Adapted from M.Porter (1985) Value Chain model – the CRM Customer Value Chain is ideally suited to professional services companies.
Related: What is customer value?
The five steps in Buttle’s CRM value chain are:
Customer Portfolio Analysis (CPA): CPA, the first step in the CRM value chain acknowledges that not all customers have equal value to the company. CPA asks the question: ‘who are our SSCs (strategically significant customers) who create long term value.
SSCs create more revenue, more value (profit) often with 80% of profit coming from 20% of customers) requiring a separate strategy for SSCs.
A Customer Portfolio comprises the mixture of groups (segments) that make up the customer base of a business.
Customer Intimacy: Long-term relationships require more knowledge about customers. Knowing about what, who, why, when and how of customer behavior is most important for a company to manage long-term relationships with loyal and strategically insignificant customers.
Network Development: A company’s network position i.e. its connectedness to other parties who co-operate in delivering value to the customer is a source of great competitive advantage.
In order to serve customer relationships, it is important for a company to create value for a customer on every stage of the selling process. It means the company must create a complete network for customers to serve profitably. A good network includes suppliers, manufacturers, employees, investors, distributors, and retailers.
Value Proposition Development: The network has to work together to create and deliver the chosen value(s) to the selected customers.
Network development by the company now will create a value proposition. Every member (actor) in a developed network works together as a whole to creating value for customers. A Value Proposition is a promise of value to be delivered, communicated, and acknowledged. It is also a belief from the customer about how value will be delivered, experienced and acquired.
Managing the Relationship: A company’s culture defines whether it will manage long term relationships or not because sometimes culture doesn’t allow it to manage relationships. Company Procurement (buying) process and HR process also suggest that how it will do such activity. Without IT and Data management process a company cannot do CRM because customer’s information and data related to customers are saved using technology.
Here are the five supporting conditions to fulfill the CRM value chain model:-
- Culture and Leadership: The leadership and culture of the business determine the focus of the business. It is up to the leaders to provide direction and prioritize CRM within an organization.
- Procurement Processes: All the tasks or activities that go on to create something of value are called processes.
- Human Resource management processes: The people in any business are the ones who interact with the customers. How they interact is one of the most important parts of CRM. Customers will at some point in time interact with staff in departments of an organisation. It is essential that the people or employees be trained to deal with customers to ensure a positive interaction.
- IT/Data management processes: CRM is totally dependent on Data and Information technology. Data provides all the insights that are essential for CRM. High-quality data is the main requirement of CRM. Data is acquired, stored, analyzed, maintained, improved, and distributed properly to be of any value to the organisation. Customer information is what drives CRM and determines all the strategies that need to be implemented for CRM. The data requirements for CRM are determined by the actions taken at the primary stages.
- Organisation design and structure
Related: Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Concepts
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.