There are several change management models that help organisations implement change successfully. Here we take a look at the various models and theories to help manage change.
Introduction to Change Management
Change management refers to changes to organisational structures or processes, and is indispensable for businesses to succeed and grow.
Since organisational change has a significant impact on the success of an organisation. Considering internal and external factors can prepare an organisation to respond to the change process effectively.
Organizations may change their designs based on internal factors and external factors. However, it is important for firms to know when to change. Initiation of a change strategy at the right time can assist firms to renew their direction, structure, meet the demands of internal and external stakeholders, and save an organisation from a downturn.
There are several models of change management and the way in which organisational change is managed can have a significant impact on the operations and staff of an organisation.
An important driver of change is the leadership style which is dependent on the srategy devised by the leader for communication, finance, production, and employee management. A good leader implements structures in order to benefiot from the positives and avoid unintended results.
Managers cannot instigate change by creating mission statements or budget plans, but rather, changes in vision, systems, and culture affect the emotions and behaviours of employees which eventually motivate them to an effective change.
Emergent and planned change
Burnes (2004) suggests two types of organisational change which include emergent and planned.
- Emergent change happens when individuals deal with breakdowns, contingencies, and re-accomplish routines in everyday work.
- Planned change occurs through participative, group- and team-based programs that aim to improve the operation and effectiveness of the human side of an organisation.
Lewin and Kotter’s change models can be linked effectively to the planned change process. However, emergent change can be applied mostly to technological companies due to their dynamic working environment which gives rise to the occurrence of constant and unexpected changes in the environment.

Change Management Models
Lewin’s Change Model
Lewin’s change model is a simple change framework, consisting of three distinct stages of change, to plan and implement the change.
The three stages are:
- Unfreeze: You create the right circumstances to make yourself ready for change
- Change: You carry out the change
- Refreeze: You adopt the new way of working.
Lewin’s Force Field Analysis
Lewin’s force field suggests that change can be characterised as a state of imbalance between driving forces as well as the opposing.restraining forces.
Here, driving forces include new technology, changing markets and consumer preferences, and so on. On the other hand, restraining forces include resistance to change (from employees), organisational inertia, fear of failure, etc.
So, if a firm wants to achieve change, it needs to carry othe these three steps:
- Unfreeze the driving and restraining forces so that they can be changed
- Introduce an imbalance by increasing the driving forces or reducing the restraining forces, or carry out both.
- Finally, once the change is implemented, both the forces are re-frozen.
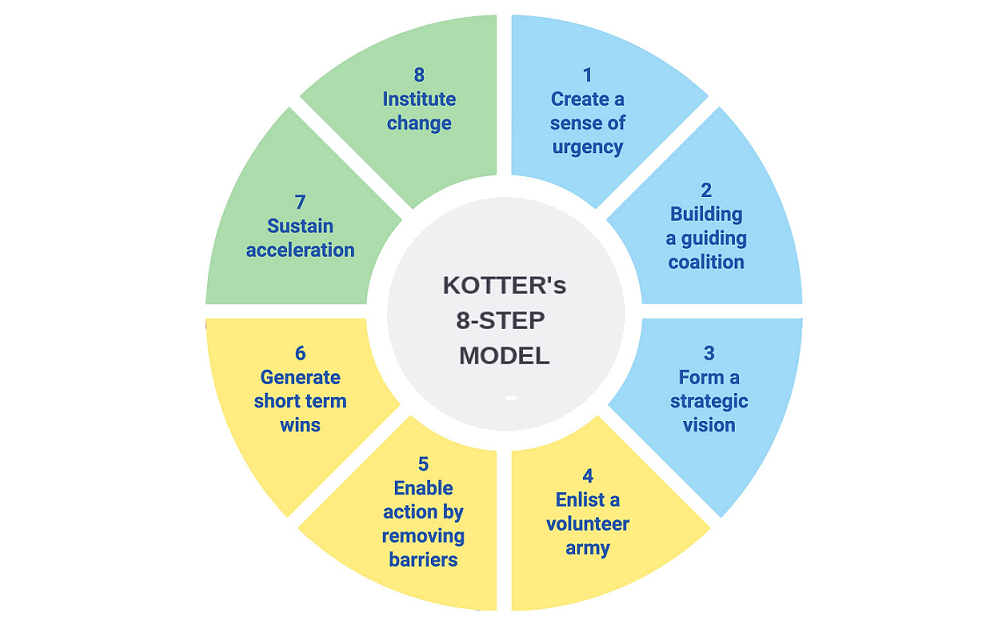
Kotter’s 8-Step Change Model
Kotter proposed an eight-step model to help leaders to create the right environment to influence change, and to develop support that will help overcome barriers and make the change happen.
Read more on Kotter’s Change Model
Leavitt’s Diamond
Leavitt’s Diamond is a theory that proposes that every organisational system is made up of four main components, people, tasks, structures and components, with an interaction among the four components. Any change in one of these components will necessitate a change in the other three components.
Here’s a video that explains Leavitt’s Diamond.
Role of HR in Organisational Change
Employees usually fear and resist organisational change. HR can play a significant role in preparing and supporting employees to change by using various methods, including leadership, training, and communication.
In firms, where managers are ill-equipped to handle change, HR can play an important role in change by supporting employees by providing them with adequate training, and developing line managers to possess the right leadership style in order to encourage employees to embrace change.
HR also helps management develop a clear command structure that encourages interactions between all levels of employees, and also supports employees in terms of their needs.
HR managers help implement communication strategies during organisational change to positively affect the perception of employees towards change. Communication could take place between managers and employees through supervision, team meetings, mentoring, coaching, and workshops.
HR provides support to employees by providing adequate training using the available resources, by creating an effective environment to support future learning, and providing learning opportunities which boosts employee commitment during organisational change.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.