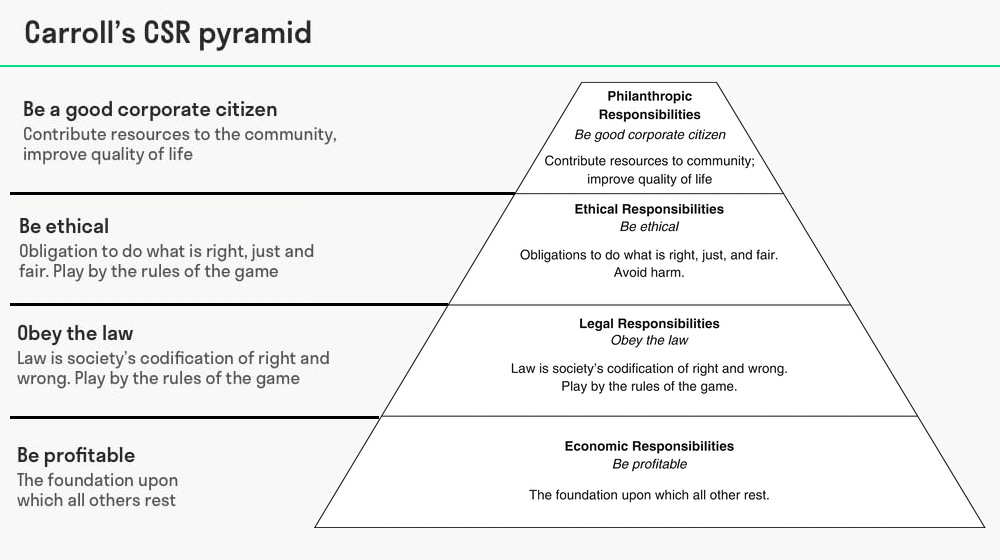
Carroll’s CSR pyramid is a framework that explains how organisations can take social responsibility, it highlights the four important types of responsibility of organisations.
The more important responsibilities are placed towards the bottom of the pyramid.
Carroll’s CSR pyramid suggests that firms should engage in practices and take responsibility at four levels – Economic, Legal, Ethical, and Philanthropic, if they really want to be seen as a responsible company.
It means the company has to be economically profitable, it should adhere to all the laws of the land, it should do what is right where the law does not provide guidance, and it should engage in philanthropic work (Carroll, 2016).
This is one of the most well-used models used to describe and explain CSR (Carroll, 1991).
According to Carroll, businesses have four levels of responsibility: economic, legal, ethical and philanthropic. Tench (2017) explains that the model can be used in conjunction with the stakeholder responsibility matrix to set out how organisations can meet their responsibilities.
The four levels of responsibilities are as follows:
Economic Responsibility
Economic responsibility of being profitable.
The responsibility of ‘Being profitable’ sits at the base of the pyramid since it is considered to be the most important for the business.
It might be surprising to say that a business has a social responsibility to make profit; yet, this is what is needed by the society. If a business is unable to meet this responsibility, it will go out of business and will not be able to contribute towards the welfare of the society.
A company should produce good quality products and offer good services to clients. It should offer safe working environment and offer fair wages to employees. It should provide reasonable returns to investors.
This is the only way to survive and benefit society in long-term. This forms the base of the pyramid upon which other responsibilities rest.
Legal Responsibility
Legal responsibility of abiding by the laws set forth by society. E.g. Employment, Competition, Health & Safety.
The ‘legal’ responsibility is ranked as the second most important responsibility in the pyramid.
The economic mission of the business must be followed by respecting the rules and regulations imposed by the local and national government.
It is important for businesses to be law abiding citizens and produce goods and services by respecting at least the minimum legal requirements. This will enable the organisation to stay away from potential penalties and fines which could impact value creation for the shareholders.
Abide by government laws, abide by federal and state regulations. Provide goods and services that meet legal requirements.
Ethical Responsibility
This refers to Ethical responsibility of performing business operations which are morally correct. Businesses should go beyond narrow requirements of the law. E.g. Treatment of suppliers & employees.
Carroll’s pyramid suggests that even if the law does not provide any guidance on some issues, a business must treat it ethically and do what is right and beneficial to the society.
Under this responsibility of the pyramid, businesses have to make sure that their operations are not harming the stakeholders in any possible way. This responsibility is vital for the well-being of the society.
Conduct business ethically. Treat employees, suppliers, clients ethically. Recognize ethical/moral norms adopted by society.
Philanthropic Responsibility
Philanthropic or discretionary responsibility is to contribute resources towards social, educational, recreational and/or cultural purposes. While discretionary, this responsibility is still important. E.g. charitable donations, staff time on projects.
Although philanthropic responsibilities are placed at the top of the pyramid (considered to be less important), these offer advantages to organisations.
The area of philanthropy is closely linked to the ethical responsibilities; most organisations engage in philanthropy to show their operations are ethical. Businesses also engage in philanthropy to show their good citizenship and to improve reputation of the company, to get an edge over its competitors. While philanthropy is not really a responsibility, in today’s world, society expects businesses to be involved in philanthropic activities.
A firm that shuns it philanthropic responsibilities is likely to be seen as an unethical company, and on the contrary, engaging in philanthropy will help improve the reputation of the firm.
Engage in CSR activities (that are more aligned with business objectives). Encourage employees to volunteer for social cause. Engage in community development efforts.
Example Matrix
Here’s an example matrix for a clothing manufacturer, using the customers as the chosen stakeholder group (Developed by Tench, 2017, p.85).
Economic: Financially well-managed company, Clear financial reporting.
Legal: Conform to consumer health and safety product guidelines (e.g. quality controls and standards for fire safety of garments, etc.) . Use Correct labelling. National and transnational product labelling eg European standards.
Ethical: Fairly priced products. Highest quality. Products are designed for and fit for purpose (eg workwear). Provide best products with the highest standards of care for employers and suppliers. Transparent sourcing of materials (no use of child labour or low-paid employees). Do not abuse suppliers or workers.
Philanthropic: Give waste products to needy organisations. Give unsold products to customers’ preferred charities or homeless groups. Support other employee or customer initiatives.
Criticism of Carroll’s Pyramid of CSR
Although considered to be the most modern representation of CSR, Carroll’s pyramid has also been criticised.
Some argue that Carroll’s pyramid cannot be used as a reference for all the businesses around the world. Global factors have not been taken into account in this pyramid. Some countries might approach CSR in a way that is different from other countries. For example, countries like Germany and Sweden give more importance to legal responsibilities, followed by economic and ethical responsibilities.
It is also argued that some messages (especially related to ethics) are repeated on every level.
Empirical evidence show that with time, the ranking of these four responsibilities is changing. Importance of ethical responsibilities have increased compared to legal and economic responsibilities over the years.
There are several corporate leaders who feel that the model is too simplistic.
However, the Carroll’s Pyramid is easy to use and understand. It conveys the message that CSR has more than one element to it, it lays its main emphasis on the aspect of profit generation.
To sum it up, Carroll’s CSR Pyramid outlines the different levels of CSR that companies can engage in. According to Carroll, firms must first fulfill their economic responsibilities before moving on to the other levels of responsibility. Businesses use this model to evaluate their CSR efforts, and to ensure that they are meeting their social obligations as corporate citizens.
References
Carroll, A.B., 2016. Carroll’s pyramid of CSR: taking another look. International journal of corporate social responsibility, 1(1), pp.1-8.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.

Leave a Reply