Consumers can often be their own “worst enemies”. Consumers’ desires, choices, and actions often result in NEGATIVE consequences to themselves and / or to society. Social pressures, a culture’s value of money, exposure to unattainable ideals of success, social status, and / or beauty – all contribute to negative consumer behavior.
Consumers are NOT always rational decision makers in the marketplace, in which they rationally obtain products and services to maximize their well-being.
Deviant Consumer behaviour
The behavior of the average consumer in an everyday consumption is normal. But sometimes consumer behavior is regarded as deviant if it is either unexpected by members of the society.
Deviant behavior may be problematic to the consumer and society. Some types of deviant consumer behavior occur during the acquisition of the product and some types occur during product consumption.
Deviant consumer behavior includes:
- addictive,
- compulsive and
- impulsive behavior,
- consumer theft,
- use of black markets and
- underage drinking and smoking.
Framework for Deviant Consumer Behavior
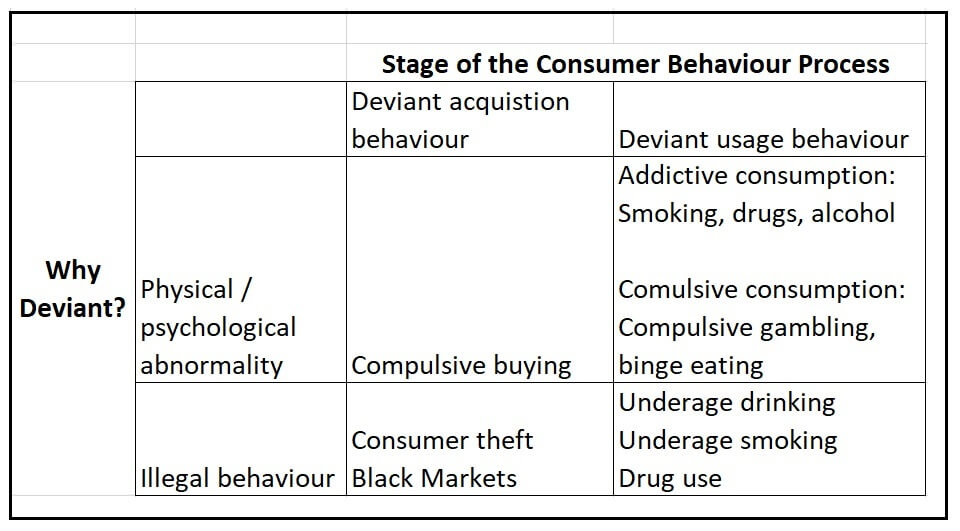
Addictive Behavior
Addictive behavior is taking action as a result of a dependency. Addicted consumers feel a great attachment to and dependence on a product or activity and believe that they must use it to function (smoking).
This is usually brought on by chemical dependency. It can be harmful to addicts and those around them. Examples: cigarettes, drugs, alcohol, Internet use and video game.
Compulsive Behavior
Compulsive behavior is an inability to stop doing something. Compulsive buying can be an emotionally involving experience. It is considered to be an ‘out-of-control’ abnormal behavior.
It includes: Repetitive shopping, excessive buying, as an antidote for depression, boredom, anxiety, or stress.
Consumers may engage in compulsive buying to feel a thrill, gain attention, or feel that they are pleasing some one else. But this emotional high may be followed serious financial and negative emotional consequences. (Gambling).
Impulsive Behaviour
Compulsive consumption is long-lasting, and different from impulsive buying which is temporary. Impulsive behavior is non thoughtful action acting on impulse. Two specific types of impulsive behavior related to acquisition and consumption are impulsive buying and impulsive eating.
An impulsive is a sudden urge to act as would happen when you find yourself doing something based on an emotional whim rather than on a reasoned, non-emotional analysis (eating habit).
Consumer Theft
Psychological factors affecting consumer theft:
Temptation to steal: The temptation to steal arises when consumers want products that they cannot legitimately buy.
Rationalization for stealing: Consumers steal because they can somehow rationalize their behavior as being either justified or driven by forces outside themselves.
Black Markets
Black markets represent situations in which consumers pay for items not readily available. These are called black markets because the sellers are unauthorized which means that the buying –selling process is usually illegal.
Example: Black markets for drugs, entertainment
Underage Drinking and Smoking
Addictions to alcohol and tobacco represent one form of deviant consumer behavior. Illegal use of these products by minors is another deviant consumer behavior. Underage drinking and smoking have consequences for the individual and for society.Marketing Implications
Marketing activities can encourage addictive, compulsive, and impulsive behavior. Some marketing activities can reduce addictive and compulsive behavior.
Activities that stimulate/reduce: Product availability. Exposure to advertising. Targeting youth. Inappropriate message in media/ads. Warning labels/ads.
BATheories.com is managed by a group of educators from Mumbai. We also manage the website StudyMumbai.com. Our panel includes experienced professionals and lecturers with a background in management. BATheories is where we talk about the various business theories and models for BA (Business Administration) students.

Leave a Reply